How To Sleep With A Thoracic Herniated Disc

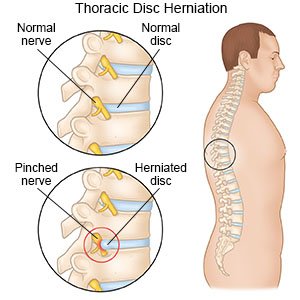
A thoracic herniated disc occurs when a spinal disc in the mid back ruptures.
How to sleep with a thoracic herniated disc. A herniated disc refers to an intervertebral disc tear that causes the nucleus pulposus central portion to rupture and irritate surrounding spinal discs and nerves. The herniated disc may press on your nerves or spinal cord. Thoracic discs are located between the base of your neck and your lower back. Each healthy disc in the spine contains a jelly like inner core called the nucleus pulposus and a tough outer coating called the annulus fibrosus.
What is thoracic disc herniation. Unfortunately pain from a herniated disc may make it hard for you to sleep. Herniated disc in the thoracic spine is pretty uncommon and the reason for that is because there are a lot of supporting structures in the thoracic spine unlike the cervical and lumbar spine. There is a lot more motion in the cervical spine as well as the lumbar spine.
Thoracic disc herniation occurs when a thoracic disc bulges out from between your vertebrae. In the thoracic spine or upper back there are eleven spongy discs positioned between the bony vertebrae. Symptoms vary depending on the affected region of the spine the number of affected discs and the nature of the injury i e a traumatic injury degenerative disc disease etc herniated disc pain is typically the result of compressed nerve roots in. That motion is limited in the thoracic spine because of.
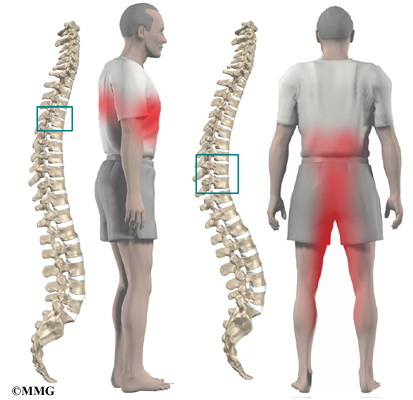
However it is most commonly found in the lumbar spine. Any time you have perineum pain numbness or tingling it means there could be pressure from your lower back onto the cauda equina which is the leftover of the spinal cord the spinal cord ends at l1 or l2 so the continuation of the spinal cord is a bunch of nerves that looks like a horse s tail thus cauda which means back or rear end and equina which refers to horse. Herniated discs can occur in the cervical thoracic and lumbar regions of the spine. This medical condition can develop anywhere in the spine including the cervical neck thoracic middle back and lumbar lower back regions.
A thoracic bulging disc is the least often seen type of intervertebral protrusion since the middle and upper back spinal regions are far less likely to develop herniated discs. A ct or mri scan to produce images of the intervertebral discs and possibly nerve root compression. However when thoracic disc bulges do occur they can be just as problematic as any other type of disc abnormalities if not more so. Diagnosis of a thoracic herniated disc may include history and physical exam diagnostic tests an x ray to eliminate other causes of pain such as a fracture.